At the present time the study of the peptides’ properties [Dudgeon W. D. et others, 2016] has a high interest. Peptides have the same structure as proteins, but the size of these molecules is smaller. It is also important to note that short peptides, being a natural metabolic product present in the body, cannot be identified in blood or urine. In this case the study of the properties of individual structures can only be provided on cell cultures.
Peptide IPH-AGAA contains a low molecular weight peptide and has myoprotective properties as well as it has a normalizing effect on muscle tissue.
Experimental studies have shown that the peptide IPH-AGAA regulates metabolic processes in myocytes, increases the reserve capacity of the body, which suggests the effectiveness of the peptide IPH-AGAA to normalize the functions of the human muscular system in disorders of various origins.
Thus, the aim of the present research was to study of myoprotective and other peptide’s properties.
Design of the study
1 stage.
To examine the cytostatic and oncological protective of the peptide IPH-AGAA properties in relation to the muscular system, we have chosen embryonic stem cells (ESCs), which are pluripotent type, which means that cells could be differentiated into all three primary germ sheets: ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm, from which the tissues of the muscular system are formed in the future. After 5 or 6 days since fertilization the human embryo reaches the blastocyst stage, from which stem cells are obtained.
The genes responsible for muscle tissue formation are the ACTN3 gene and the MSTN gene.
The ACTN3 gene encodes the protein alpha-actinin-3 (ACTN3), which stabilizes the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscles and participates in a large number of metabolic processes. Localization of the gene is on the chromosome 11q13.2. The fast muscle fibers synthesized protein alpha-actinin-3, which is encoded by the gene ACTN3. Alpha-actinin-3 stabilizes the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscles and is involved in various metabolic processes. As a result of the nonsense mutation, the codon encoding the amino acid arginine is converted into a stop codon and the synthesis of the polypeptide chain of the protein stops, which entails the absence of the alpha-actinin-3 protein in the muscles. According to that it is assumed that the polymorphism of the gene ACTN3 is one of the causes of changes in metabolism in muscle tissue and reduce the level of development of speed-power qualities in humans. On these data, we decided to study the activity of this gene in the application of the peptide IPH-AGAA.
Myostatin in humans is encoded in the MSTN gene. Myostatin (growth and differentiation factor 8) is a protein that inhibits the growth and differentiation of muscle tissue. Experimental studies show that blocking the action of myostatin leads to a significant increase in dry muscle mass with almost complete absence of fat tissue. Myostatin is active in skeletal muscles, released into the blood, exerting its effect on the muscles by binding to the receptors ACVR2B (activin type II receptor), before and after birth. This usually limits muscle growth, ensuring the absence of hypertrophied muscle tissue. On these data, we decided to study the activity of this gene in the application of the peptide IPH-AGAA.
We evaluated the expression of genes responsible for the ontogenesis of the muscular system.
2 stage.
The second stage of our experimental study was the evaluation the marker biological active molecules by immunofluorescence method using primary antibodies to Mif5 (1:150, Abcam), to ACTN3 (1:250, Abcam) and p53 protein (1:50, Abcam).
We have selected the following marker biologically active molecules:
1) Protein Mif5 (Myogenic factor 5) is a key transcription factor in the regulation of skeletal muscle myogenesis. It belongs to the family of myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs), which also includes proteins MyoD(Myf3), myogenin, MRF4 (Myf6). Mif5 is the earliest differentiation factor and begins to be expressed in embryogenesis from all the transcription factors in The MRFs family. Mif5 induces differentiation of polypotent myogenic cells in the direction of skeletal muscles [Kim A. R. et al., 2017].
2) The protein alpha-actinin-3 (ACTN3) stabilizes the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscles and participates in a large number of metabolic processes. Alpha-actinin 3 binds actin fibers in muscle and is found only in white muscle fibers, increasing their contractility and strength [Kathryn R Wagner, 2018].
3) Aging of polypotent cells in culture is associated with increased activity of the p53 gene. In mice with mutation in the p53 gene, there was increased resistance to the development of tumors, combined with a reduction in life expectancy. P53 protein plays a key role in endogenous antitumor mechanisms [Donekover et al., 2002]. P53 protein controls the course of cell cycle processes, as well as the absence of damage in the genome that could lead to further development of pathology. Protein p53 is a transcriptional factor that serves as a suppressor of malignant tumors by activating apoptosis in the tissues of the body. The p53 protein is activated when DNA is damaged, as well as when there are factors that can lead to such damage or are any signals of cell aging and a disorders of its functional activity [Arshad H. et al., 2010]. P53-dependent apoptosis avoids the accumulation of mutations, and, when they have already occurred, p53-dependent apoptosis allows to eliminate such potentially dangerous cells [Burtis C., Ashwood E., Bruns D., 2006].
Research
To study the peptide IPH-AGAA properties we used the following cell cultures of the Russian collection of vertebrate cell cultures (RCVCC):
SC5
Origin: human, embryonic stem cells (ESCs), blastocyst (5-6 days of growth), obtained as a result of IVF
Science. 1998. 282: 1145 – 1147; Ontogenesis. 2011. 42 (4): 249 – 263;
Cytology. 2012. 54 (1): 5 – 16.
Morphology: colonies of rounded cells with high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio.
Method of cultivation: monolayer; colonies attached to mitotically inactivated (mitomycin-C) feeder layer of mesenchymal cells of the bone marrow of the human embryo.
Cultivation conditions: medium — Knockout Dulbecco’s modified Eagles medium serum — Knockout Serum Replacement 20% other ingredients – NEAA 1%, L-glutamine 2mM, 2 — mercaptoethanol 0.1 mM, bFGF — 8 ng/ml
The procedure of reseeding – mechanical replanting of ESC culture was carried out under the control of a microscope by dividing the colony into fragments using a disposable scalpel and transferring them to a new layer of the feeder; daily change of environment, reseeding every 5-6 days.
Cryopreservation — growth medium, 10% DMSO, 5×105 cells/ml in ampoule.
Viability after cryopreservation: 60 % (trypan blue on the zero passage)
Control of contamination: bacteria, fungi and Mycoplasma were not detected.
Control of the identity of the species: karyological analysis.
Karyology: 2n= 46, modal chromosome number 46 (98.0+0.9 %), normal human karyotype (46, XX), number of polyploids (0.2 + 0.2%).
DNA profile (STR): Amelogenin: X, X
CSF1PO: 12, 13
D13S317: 8, 11
D16S539: 9, 12
D5S818: 9, 11
D7S820: 8,10,12
THO1: 6, 9.3
TPOX: 10, 11
vWA: 17,17
Other characteristic:
The average time of one cell population doubling is 28.2 hours.
Immortalized line passed more than 120 doubling the cell population.
Expression of surface antigens typical for human ESCs: SSEA-4, TRA-1-60 and transcription factors Oct-4, Nanog.
The ability to spontaneously differentiate into derivatives of 3 germ leaves.
Ability to form in vivo teratomas containing derivatives of 3 germ leaves.
Field of application: cell biology, embryology.
Collections: Institute of Cytology of the Russian Academy of Sciences (figure 1) (Federal state budgetary institution of science «Institute of Cytology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, http://www.cytspb.rssi.ru/eotk/infbull_ru.htm , M. S. Bogdanova, G. G. Polyanskaya, A. M. Koltsova «Cell cultures» Newsletter. Issue. 34 (2018), http://www.cytspb.rssi.ru/rkkk/katalog1n_2017_with_figs.pdf).
Method of research
Group for the study:
Group 1 – the measurement of the expression of molecules before the study,
Group 2 — control (addition of nutrient medium, serum albumin incubation),
Group 3 – addition of the control peptide of Glu-Trp dipeptide at a concentration of 100 micrograms (µg);
Group 4 – addition of IPH-AGAA peptide at a concentration of 100 micrograms (mcg).
The study used peptides IPH-AGAA and Glu-Trp in the form of a lyophilized powder, which were dissolved with sterile water for injection in a volume of 10 ml to a final peptide concentration of 100 mcg.
For most dissociated cell cultures, as previously shown, the most effective is the peptide concentration of 100 mcg/ml based on long-term experience with peptides [Linkova N. S. et al., 2016; Khavinson V. et al., 2017].
For the control immuno protective peptide Glu-Trp has been selected which properties are known and well described in the literature [Morozov V. G., Khavinson V. Kh., Malinin V. V., 2000, Khavinson V. Kh., Morozov V. G., 2001, Khavinson V. Kh., Kuznik B. I., Linkova N. S., Pronyaeva V. E., 2013].
PCR-method with the use of Own primers and Novocasta reagents and sets of monoclonal antibodies (production by the firm Biosource (Belgium) were used to measure the level of gene expression.
Cell smears were treated with appropriate primary antibodies according to the standard Protocol:
- Triple washing with phosphate-salt buffer — FSB(pH=7,2) for 5 min
- Permeabilization of cells with 0.1% Triton X-100, dissolved in the FSB, for 15 min.
- Rinsing in three changes of the FSB (for 5 min.)
- Incubation in 1% bovine serum albumin (diluted FSB, pH 7.5) for 30 min to block nonspecific binding;
- Incubation with primary antibodies, 60 min;
- Rinsing in three changes of the FSB (for 5 min.)
- Incubation with secondary antibodies conjugated with fluorochrome Alexa Fluor 488 (1:1000, Abcam) 30 min at the room temperature in the dark;
- Rinsing in three changes of the FSB (for 5 min.);
- staining the cell nuclei with Hoechst 33258 dye (Sigma, USA) (1:100 from the waste solution in dH2O) for 1 min (the dye is used as a fluorescent DNA marker, when binding to which its fluorescence increases).
- Rinsing in FSB (for 5 min.);
- packaging of prepared spicemen under cover glass in the mounting medium Dako Fluorescent Mounting Medium (Dako).
The study of specimen was carried out in the confocal microscope Olympus FluoView FV1000 at an increase of 200, 400, 600. Blue color fluoresces the expression of the studied marker. Conducted measurement of the relative areas of expression in %. The relative area of expression was calculated as the ratio of the area occupied by immuno positive cells to the total area of cells in the field of view and expressed as a percentage. The dynamics of gene expression is measured in conventional units, the base level is taken as 10.
Statistical processing of results
Statistical processing of experimental data included calculation of arithmetic mean, standard deviation and confidence interval for each sample and was carried out in Statistica 11.0. If the data were normally distributed, the differences in means were determined by the Student test (t).
Research results and discussion
The effect of the peptide IPH-AGAA on the expression of genes responsible for the formation of a system of human muscle
Thus, in figure 2, we show that the peptide IPH-AGAA significantly increases the expression of the gene ACTN3, responsible for the normal formation and formation of the muscle system, in particular, regulating metabolism in muscle tissue and the level of development of speed-strength qualities in humans, which also allows to optimize metabolism in muscle cells and provide antioxidant action, with exercise to prevent damage to muscle cells by free radicals.
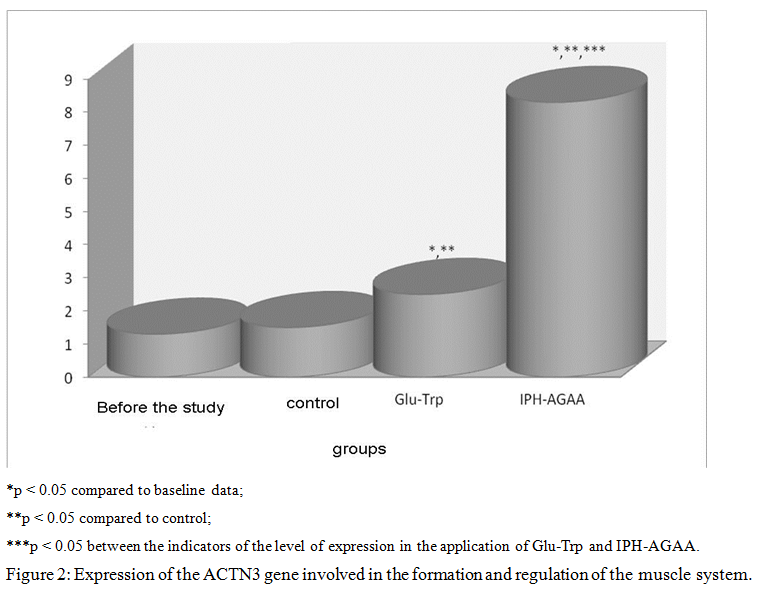
Thus, in figure 3, we show that the peptide IPH-AGAA significantly increases the expression of the MSTN gene that controls the growth of muscle mass, in particular, guaranteeing the absence of hypertrophied muscle tissue.
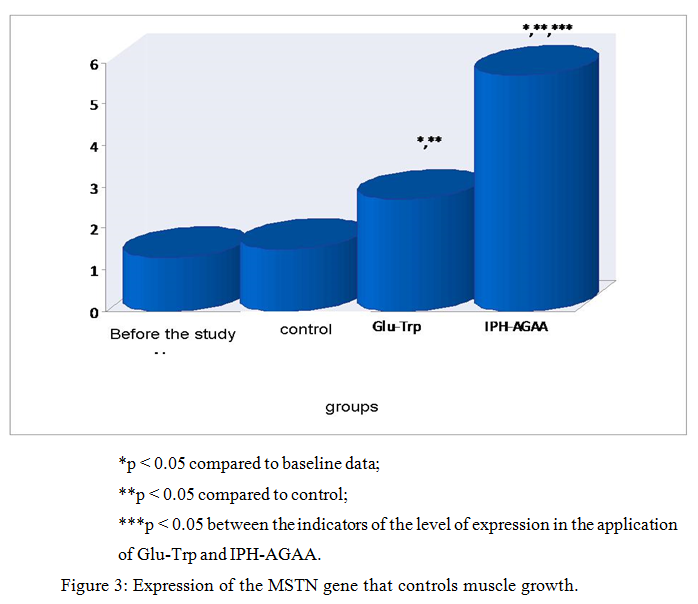
Thus, from the above data it can be seen that under the influence of the peptide IPH-AGAA in human cell culture there is a statistically significant increase in the expression of genes responsible for the ontogenesis of the muscular system. These data show that the peptide IPH-AGAA significantly increases in the culture of human cells «cascade» of signal molecules, which is necessary to activate the processes of proliferation and differentiation of stem cells in the cells of the muscular system, the formation of muscle system, regulation of metabolism in muscle tissue and thus determine the level of development of speed-strength in humans.
The effect of the peptide IPH-AGAA to Mif5 protein expression in cultures of human cells
Figure 4 shows that the use of the peptide IPH-AGAA increases the expression of Mif5 in 4 times from the baseline, which is a key transcriptional factor in the regulation of skeletal muscle myogenesis.
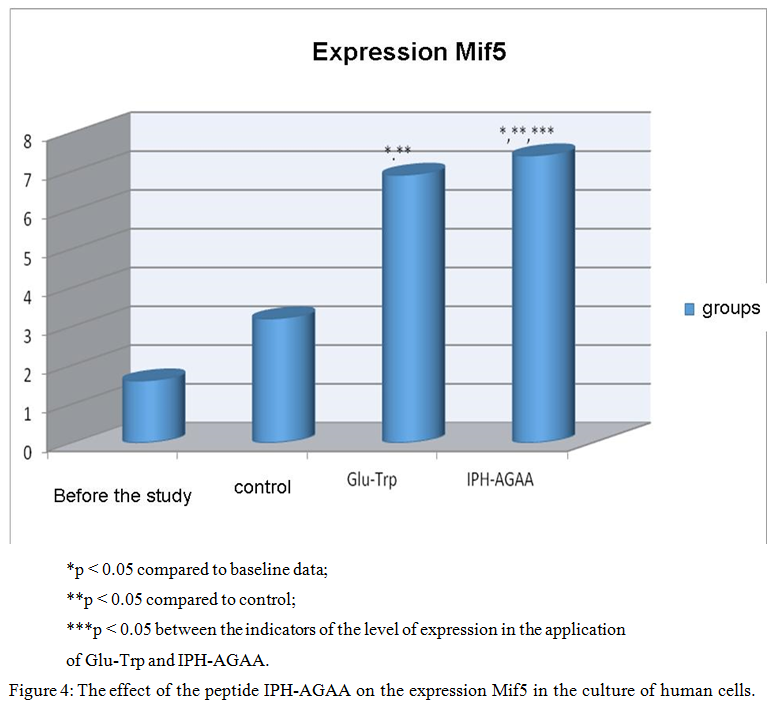
Thus, the use of peptide IPH-AGAA has biologically protectors’ character, in particular, induces myogenic differentiation of pluripotent cells towards the normal formation of skeletal muscle and provides intense and long lasting nourishment to the cells of the muscle tissue.
The effect of the peptide IPH-AGAA on the expression of ACTN3 protein in cultures of human cells
Figure 5 presents that the use of IPH-AGAA peptide significantly increases the expression of ACTN3 protein in 4.5 times from the initial level, which stabilizes the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscles and participates in a large number of metabolic processes, which leads to the optimization of metabolism in muscle cells, improve microcirculation in muscle tissue and restore water and mineral balance in muscles.
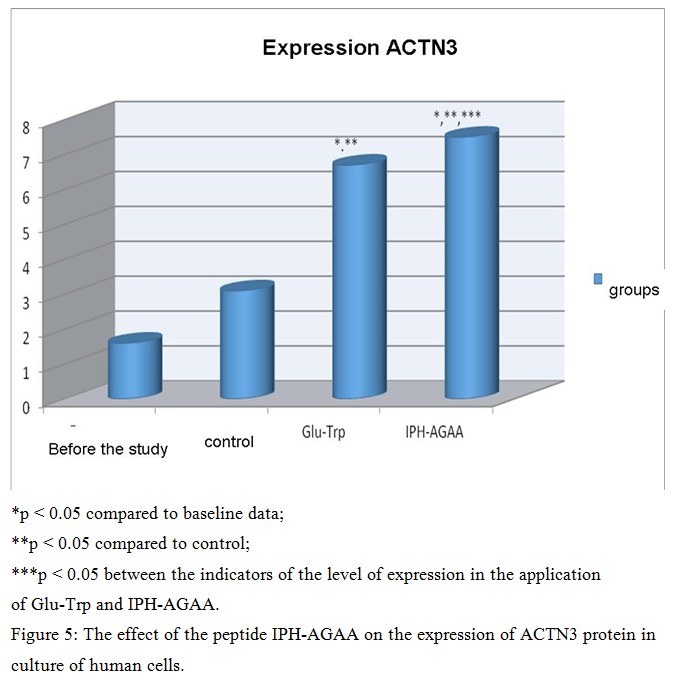
Thus, the use of the peptide IPH-AGAA has a myoprotective nature, in particular, increasing the activity of actin fibers in the muscle, increasing the contractility and strength of muscle tissue, thereby increasing the elasticity and elasticity of the muscles and providing a stimulating effect on the muscles in hypoxia.
The effect of the peptide IPH-AGAA on the expression of p53 protein in cultures of human cells
Figure 6 presents the use of the peptide IPH-AGAA increases the production of protein p53, which is a transcriptional factor that serves as a suppressor of malignant tumors by activating apoptosis in the tissues of the body, which allows us to conclude about the antitumor properties of the studied peptide.
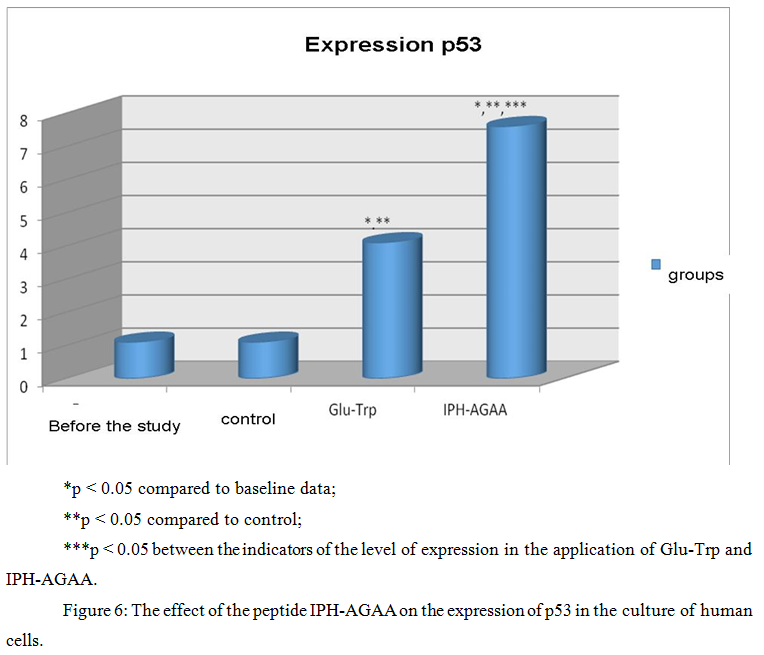
P53-dependent apoptosis also avoids the accumulation of mutations, and, in the case where they have already arisen, p53-dependent apoptosis allows to eliminate such potentially dangerous cells for the body, which leads to the conclusion about the cytoprotective effect of the studied peptide.
The data indicate a high oncological protective activity of the peptide IPH-AGAA in relation to the cells of the muscles according to the expression of biological molecules in cell culture.
Conclusion
The performed studies confirm the high biological activity of the peptide IPH-AGAA in relation to the control of the normal formation of the muscle system in humans at the genetic level according to the expression of genes responsible for the ontogenesis of the muscular system. In particular, these data confirm that the use of the peptide IPH-AGAA regulates metabolism in muscle tissue and the level of development of speed-power qualities in humans, which also allows to optimize the metabolism in muscle cells and provide antioxidant action, physical activity to prevent damage to muscle cells by free radicals.
Peptide IPH-AGAA significantly increases in human cell culture «cascade» of signal molecules, which is necessary to activate the processes of proliferation and differentiation of stem cells in the cells of the muscular system, the formation of muscle system, regulation of metabolism in muscle tissue and thus determine the level of development of speed-power qualities in humans.
The use of the peptide IPH-AGAA has a myoprotective character, in particular, induces differentiation of polypotent myogenic cells in the direction of normal formation of skeletal muscles and provides intensive and long-term nutrition of muscle cells. The use of the peptide IPH-AGAA leads to optimization of metabolism in muscle cells, improvement of microcirculation in muscle tissue and restoration of water and mineral balance in muscles.
The use of the peptide IPH-AGAA has myoprotective nature, in particular, increasing the activity of actin fibers in the muscle, increasing the contractility and strength of muscle tissue, thereby increasing the elasticity and elasticity of muscles and providing a stimulating effect on muscles in hypoxia.
The data indicate a high oncological protective activity of the peptide IPH-AGAA in relation to the cells of the muscles according to the expression of biological molecules in cell culture.
Literature
- Linkova N. S., Drobantseva A. O., Orlova O. A., Kuznetsova E. P., Polyakova O. V., Kvetnoy I. M., Khvinson H. Kh. Peptide regulation of functions of skin fibroblasts upon aging in vitro // Cell technologies in biology and medicine. – 2016. — №1. P 40-44.
- Mutovin G. R. Fundamentals of clinical genetics (genomics and proteomics of hereditary pathology). Textbook for universities in 2 volumes. Issue. 3. M.: GEOTAR-media 2008.
- Khavinson V. Kh. Peptide regulation of aging. SPb.: Science, 2009. – P 50
- Ahmetov II, Druzhevskaya AM, Astratenkova IV, Popov DV, Vinogradova OL, Rogozkin VA. The ACTN3 R577X polymorphism in Russian endurance athletes. Br J Sports Med. 2010 Jul;44(9):649-52.
- Arshad H., Ahmad Z., Hasan S.H. Gliomas: correlation of histologic grade, Ki67 and p53 expression with patient survival // Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. – 2010. – Vol. 11. – N 6. – P. 1637-1640;
- Kathryn R Wagner, MD, PhD and Julie S Cohen, ScM, CGC. Myostatin-Related Muscle Hypertrophy// National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine- 2018.- № 4- 35-39.
- Kim A.R., Kim K.M., Byun M.R., Hwang J.H., Park J.I., Oh H.T., Kim H.K., Jeong M.G., Hwang E.S., Hong J.H. Catechins activate muscle stem cells by Myf5 induction and stimulate muscle regeneration // Biochem Biophys Res Commun. – 2017. – Vol. 489, N 2. – P. 142-148.
- Meienberg J, Rohrbach M, Neuenschwander S, Spanaus K, Giunta C, Alonso S, Arnold E, Henggeler C, Regenass S, Patrignani A, Azzarello-Burri S, Steiner B, Nygren AO, Carrel T, Steinmann B, Mátyás G. Hemizygous deletion of COL3A1, COL5A2, and MSTN causes a complex phenotype with aortic dissection: a lesson for and from true haploinsufficiency. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010;18:1315–21.




