Peptide IPH PRO contains a complex of low molecular weight peptides and has a normalizing effect on prostate function.
Experimental studies have shown that the peptide IPH PRO is regulated by the metabolic processes in the prostate cells, increasing their spare capacity, suggesting that the efficacy of peptide IPH PRO to normalize the functions of the prostate gland in men of different ages in disorders of various origins.
Prostate diseases currently occupy a significant place among urological diseases, tend to increase morbidity and acquire increasing social significance. According to some authors, more than 60% of men over the age above 50 years old suffer from diseases of the prostate, in particular, have chronic prostatitis.
A great influence on the development of chronic prostatitis has a breakdown of the body adaptive abilities, which occurs during stress reactions and hypodynamia. There is a hemodynamic theory of prostatitis, which is due to stagnation and the introduction of infection agents.
No less dangerous for the social life of men is the development of chronic prostatitis. Chronic prostatitis affects more than 50% of the male population. Chronic prostatitis often affects men aged from 20 to 40 years, who are in the period of greatest sexual, reproductive and labor activity, which repeatedly proves not only medical, but also socially significant aspect of the correction of this condition, and hence the search for new means of therapeutic and preventive measures.
Characteristics of the study
The most frequently used type of laboratory animals for the study of peptide properties, recommended by the Ministry of health of the Russian Federation in the Manual on pre-clinical trials of drugs [Mironov A. N., Bunatyan N. D. et al., 2012], are rats, as pharmacokinetic processes are similar to those in humans. To study the properties of the peptide IPH PRO, we created a model of hypokinetic stress, in which experimental rats developed prostatitis.
We have studied 40 rats at the age of 14,2±1,2 months and at the weight of 409,6±9.5 g, which was created by the hypokinetic stress conditions for the development of prostatitis duration of 12 days by placement in special Plexiglas cages — a pencil with the dimensions: 140×60×60 mm for each rat, where males daily were in a state of immobilization.
Daylight was 12 hours. For food animals used complete feed for rodents with additional feeding in the form of fruits and vegetables. Water was used by animals independently from drinkers. Food and liquid were taken by animals ad libitum. Current cleaning of cells was carried out daily. General cleaning with disinfection of cells was performed weekly. All procedures of keeping animals, manipulations and testing of the obtained data were carried out in accordance with the standards ISO 10993-1-2003 and state standard RISO 10993.2-2006.
Rats were divided into 2 groups – control (n=20) and main (n=20). The rats of the main group were orally taking through a pipette dispenser, which allows to control the volume and the fact of liquid consumption, a drug consisting of water for injection in a dosage of 1 ml, in which the lyophilized powder of IPH PRO peptides in a concentration of 0.59 micrograms (µg) per rat body weight per day (minimum dosage, in which there are signs of improvement in the indices of the long-term experience of the use of peptides), for 14 days. The medicine was administered per os directly into the oral cavity under supervision and tracking its ingestion.
After 26 days, the rats were killed, then the prostate was removed, fixed by immersion in a solution of 4% paraphore maldegide in a phosphate buffer (PBS pH = 7.3) for 24 hours at a temperature of 4’C. Produced slices with a thickness of 20 µm using cryotome of Leica CM 1510S model (Germany). The sections were then mounted on a slide and stained with hematoxilin and eosin.
For the study we used the microscope Olympus IX81. The microscope was equipped with a digital camera Olympus DP72 (Japan), connected to a personal computer. Photo and video recording of technological processes (experimental processes) with animals was not carried out in accordance with the principles of biomedical ethics and due to the lack of permission of the ethical Committee.
Statistical data processing
To assess the reliability of the difference in the results obtained in the groups before the medicine admission, compared with the groups after the medicine admission, the Dunnet criterion was used.
Research result
During the experiment, we found that in the control group in the stroma of the prostate, significant areas of leukocyte infiltration were noticeable, which amounted to a distribution area of 76.8±1.2%. While in rats injected with the peptide IPH PRO, the area of leukocyte infiltration was 41.4±0.4% (figure 1).
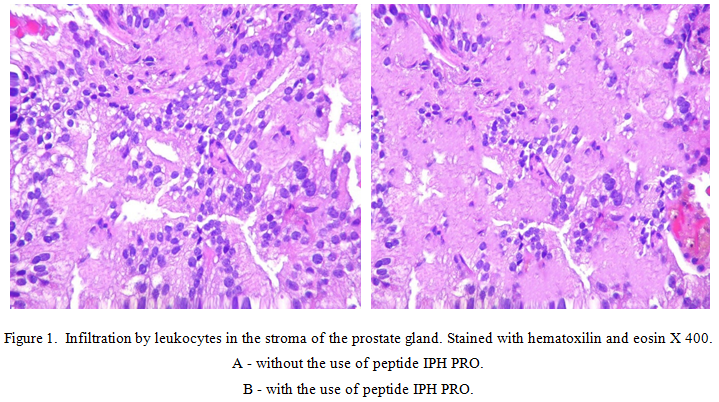
Thus, the peptide IPH PRO reduces the degree of inflammation in the development of prostatitis on the experimental model.
In the study of the capillary channel, we found that, in addition to the developed thickening and edema of tissues, there were areas of necrotic endothelial cells, the accumulation of amyloid plaques. All these morphological parameters indicate a sharp decrease in reparative capabilities within cells.
To assess the normalizing effect of the peptide IPH PRO, we studied the cross-sectional area of the arterial channel (figure 2).
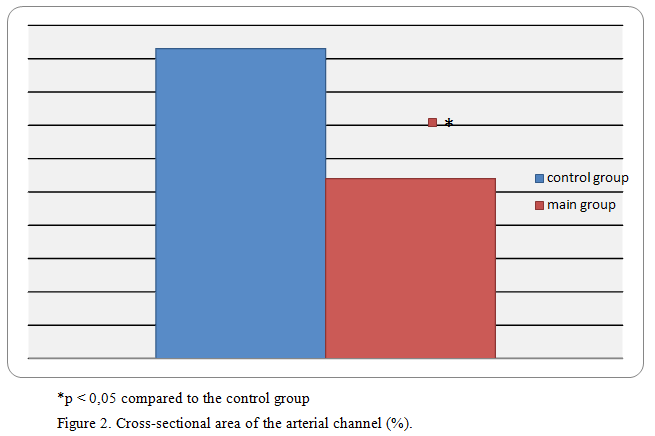
Thus, we have found that rats treated with peptides IPH PRO had in 1.7 times smaller cross-sectional area of the arterial channel than rats with prostatitis without treatment. Given the sharp decrease in the reparative capabilities of epithelial cells, it can be concluded that such a decrease in the area of the arterial channel indicates a lower need for compensatory reactions, which are manifested by an increase in the cross-sectional area of blood vessels under stress.
Appropriately, the peptide IPH PRO has a cytostatic effect and increases the adaptive capacity of cells in rats with prostatitis according to experimental data.
Conclusion
Thus, the peptide IPH PRO has a regulating effect on the functional activity of male genital cells, which leads to a cytostatic and anti-inflammatory action against prostate cells according to experimental studies.
Literature
- Mironov A. N., Bunatyan N. D. etc. Guidelines for preclinical studies of the drugs// the Team of authors. — M.: Grif and K, 2012. — 944 p.
- Khavinson V. Kh., Kuznik B. I., Linkova N.S. Pronyaeva V. E. Effect of peptide regulators and cytokines on life expectancy and age-related changes in hemostasis. // Advances of phisiology sciences’. 2013. Vol. 44. 1. P. 39-53.
- Kageyama S, Ii H, Taniguchi K, Kubota S, Yoshida T, Isono T, Chano T, Yoshiya T, Ito K, Yoshiki T, Kawauchi A, Nakata S. Mechanisms of Tumor Growth Inhibition by Depletion of γ-Glutamylcyclotransferase (GGCT): A Novel Molecular Target for Anticancer Therapy// Int J Mol Sci. -2018 — № 19(7). –p.20-34.
- Sarma, A.V. Clinical Practice. Benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms / AV Sarma, Wei JT / / N. Engl. J. Med. — 2012 -. 367, № 3 -. P. 248-257.




